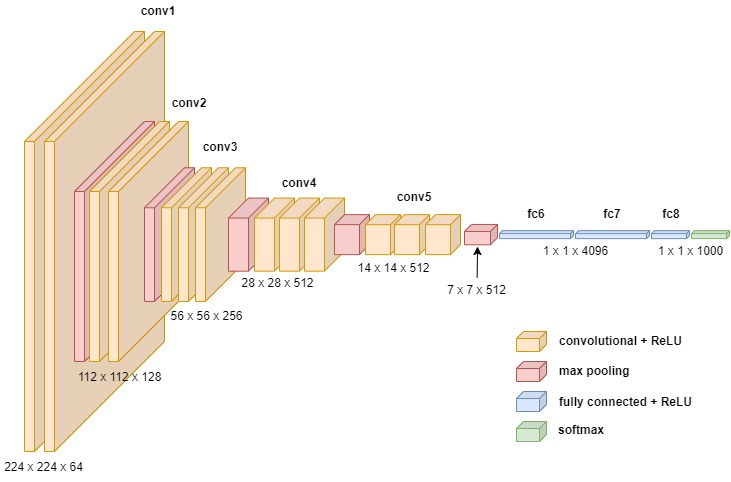
🔍 Introduction
PyTorch is one of the most widely used deep learning frameworks, known for its dynamic computation graph, ease of debugging, and native support for Python. While beginners often start with basic models like linear regression or simple feedforward networks, advanced users leverage PyTorch for complex tasks like custom model development, distributed training, and optimization strategies. This guide provides an in-depth look at advanced PyTorch concepts to help you build scalable and high-performance deep learning solutions. 💡
🧱 1. Understanding the Computational Graph in PyTorch
PyTorch uses a dynamic computation graph, often referred to as “define-by-run.” This means the graph is built on-the-fly during the forward pass and can vary with each iteration.
Key Benefits:
- 🛠️ Flexibility: Easily adapt models to different tasks.
- 🔍 Debugging: Use standard Python debugging tools (like
pdb). - 🧪 Experimentation: Modify architectures dynamically without re-compiling the graph.
python -------- import torch x = torch.tensor([2.0], requires_grad=True) y = x ** 2 + 3 * x + 4 y.backward() print(x.grad) # Gradient with respect to x
Here, PyTorch automatically computes the gradients using autograd.
🏗️ 2. Custom Model Architectures with nn.Module
While Sequential models are great for prototyping, custom models offer flexibility and control. Inherit from torch.nn.Module to define your own layers and forward pass.
python
--------
import torch.nn as nn
class CustomNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CustomNet, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Linear(100, 50)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.layer2 = nn.Linear(50, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.layer1(x))
return self.layer2(x)
Advantages:
- 🔄 Full control over forward computation
- ⚙️ Ability to integrate complex operations
- 🔁 Easy to wrap in training loops or pipelines
🧠 3. Advanced Loss Functions and Metrics
Moving beyond standard loss functions like MSE or CrossEntropy, you may want to define your own loss for custom tasks.
python
--------
def custom_loss(output, target):
return torch.mean((output - target)**2 + 0.1 * torch.abs(output - target))
Also, implement evaluation metrics like:
- 🎯 Accuracy
- 🔍 Precision, Recall, F1 Score
- 📉 AUC-ROC for classification tasks
Use torchmetrics or build your own using PyTorch operations.
🚅 4. GPU Acceleration and Multi-GPU Training
PyTorch provides easy APIs for moving data and models to GPUs:
python
--------
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = CustomNet().to(device)
inputs = inputs.to(device)
For multi-GPU training:
python -------- model = nn.DataParallel(CustomNet()).cuda()
And for massively parallel training, explore torch.distributed for distributed data parallelism. 🧵⚙️
🏁 5. Custom Training Loops with Optimizers and Schedulers
Writing custom training loops gives you flexibility in managing epochs, batch sizes, and early stopping.
python
--------
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=10, gamma=0.1)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for batch in dataloader:
inputs, targets = batch
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
Use schedulers like:
- 🔁
StepLR - 📉
ReduceLROnPlateau - 🚀
CosineAnnealingLR
📦 6. Model Checkpointing and Serialization
Save and load model weights using torch.save and torch.load.
python
--------
# Saving
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model.pth')
# Loading
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model.pth'))
model.eval()
For complete reproducibility, also save:
- ⚙️ Optimizer state
- 🔁 Epoch number
- 📊 Validation metrics
🔄 7. Data Handling and Augmentation
Using torch.utils.data.Dataset and DataLoader allows for efficient data batching, shuffling, and parallel loading.
python
--------
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
class CustomDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data, labels):
self.data = data
self.labels = labels
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.data[idx], self.labels[idx]
dataloader = DataLoader(CustomDataset(data, labels), batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
For image and text tasks, integrate with:
- 🖼️
torchvision.transforms - 📚
torchtextfor NLP tasks
🚀 8. Hyperparameter Tuning and Experimentation
Use tools like:
- 🧪 Optuna
- 📈 Ray Tune
- 🧰 Weights & Biases (wandb) for logging
Track:
- Learning rate
- Number of layers
- Dropout rates
- Regularization
Example with Optuna:
python
--------
import optuna
def objective(trial):
lr = trial.suggest_loguniform('lr', 1e-5, 1e-2)
# Train model with this lr
return validation_accuracy
🧩 9. PyTorch Ecosystem Extensions
Explore:
- 🧪 TorchVision: Image models and transforms
- 📖 TorchText: NLP datasets and processing
- 🎵 TorchAudio: Audio classification and processing
- 📊 TorchMetrics: Evaluation metrics
- ⚡ PyTorch Lightning: Clean abstraction for training logic
📐 10. Deploying PyTorch Models
For production:
- Convert to TorchScript for deployment
- Use ONNX for cross-platform inference
- Deploy with TorchServe, FastAPI, or Flask
python -------- scripted_model = torch.jit.script(model) torch.jit.save(scripted_model, 'scripted_model.pt')
Deploy models on:
- 🖥️ Edge devices
- ☁️ Cloud platforms (AWS, GCP)
- 🎛️ Mobile (with PyTorch Mobile)
🧭 Conclusion
Advanced PyTorch usage opens the door to high-performance deep learning systems tailored for real-world tasks. From building custom architectures to leveraging GPUs, managing complex training pipelines, and deploying models in production, PyTorch provides all the tools necessary for success. 🧠⚙️
Master these advanced techniques, and you’ll be well-equipped to tackle cutting-edge AI challenges in research and industry alike. 🚀💼